| [1]Matsunaga K, Usui A, Yamaguchi K, et al. An anatomical study of the muscles that attach to the articular disc of the temporomandibular joint. Clin Anat. 2009;22(8):932-940.
[2]Tanaka E, Hirose M, Inubushi T, et al. Effect of hyperactivity of the lateral pterygoid muscle on the temporomandibular joint disk. J Biomech Eng. 2007;129(6):890-897.
[3]Wang L, Pan J, Wang T, et al. Pathological cyclic strain-induced apoptosis in human periodontal ligament cells through the RhoGDIalpha/caspase-3/PARP pathway. PLoS One. 2013;8(10):e75973.
[4]Rust C, Gores GJ. Apoptosis and liver disease. Am J Med. 2000;108(7):567-574.
[5]Liu J, Wang Y, Yuan X, et al. Cyclic-stretch induces the apoptosis of myoblast by activation of Caspase-3 protease in a magnitude-dependent manner. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2010;42(12):2004-2011.
[6]唐惠玲.线粒体介导的细胞凋亡的研究进展[J].安徽医药,2012, 16(11):1696-1699.
[7]Jiang X, Wang X. Cytochrome C-mediated apoptosis. Annu Rev Biochem. 2004;73:87-106.
[8]Huttemann M, Helling S, Sanderson TH, et al. Regulation of mitochondrial respiration and apoptosis through cell signaling: cytochrome c oxidase and cytochrome c in ischemia/reperfusion injury and inflammation. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2012;1817(4):598-609.
[9]Gu S, Zhao Y, Guo J, et al. High expression of APAF-1 elevates erythroid apoptosis in iron overload myelodysplastic syndrome. Tumour Biol. 2014;35(3): 2211-2218.
[10]Sun KW, Ma YY, Guan TP, et al. Oridonin induces apoptosis in gastric cancer through Apaf-1, cytochrome c and caspase-3 signaling pathway. World J Gastroenterol. 2012;18(48):7166-7174.
[11]Shoshan-Barmatz V, Keinan N, Abu-Hamad S, et al. Apoptosis is regulated by the VDAC1 N-terminal region and by VDAC oligomerization: release of cytochrome c, AIF and Smac/Diablo. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2010;1797(6-7): 1281-1291.
[12]王辉,张琳,沈树娜. Caspases家族在妇科疾病中的研究进展[J]. 医学综述,2012,18(9):1314-1316.
[13]Porter AG, Janicke RU. Emerging roles of caspase-3 in apoptosis. Cell Death Differ. 1999;6(2):99-104.
[14]Salakou S, Kardamakis D, Tsamandas AC, et al. Increased Bax/Bcl-2 ratio up-regulates caspase-3 and increases apoptosis in the thymus of patients with myasthenia gravis. In Vivo. 2007;21(1):123-132.
[15]Renatus M, Stennicke HR, Scott FL, et al. Dimer formation drives the activation of the cell death protease caspase 9. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2001;98(25):14250-14255.
[16]Acehan D, Jiang X, Morgan DG, et al. Three-dimensional structure of the apoptosome: implications for assembly, procaspase-9 binding, and activation. Mol Cell. 2002; 9(2): 423-432.
[17]田臻,杨竹丽,贾文敏,等. p38MAPK信号通路与应力介导成肌细胞的凋亡(英文)[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2011, 15(15):2751-2754.
[18]阎潇. Caspase-3在应力介导的成肌细胞凋亡中的作用及其机制[D].青岛:青岛大学,2012.
[19]Khan A, Farah CS, Savage NW, et al. Th1 cytokines in oral lichen planus. J Oral Pathol Med. 2003;32(2):77-83.
[20]胡锴,刘好朋,万婷,等. 线粒体与细胞凋亡的关系[J].中国畜牧兽医,2010,37(12):86-88.
[21]Czerniczyniec A, Bustamante J, Lores-Arnaiz S. Improvement of mouse brain mitochondrial function after deprenyl treatment. Neuroscience. 2007;144(2):685-693.
[22]Bellido T, Huening M, Raval-Pandya M, et al. Calbindin-D28k is expressed in osteoblastic cells and suppresses their apoptosis by inhibiting caspase-3 activity. J Biol Chem. 2000;275(34):26328-26332.
[23]朱炎杰,高维娟. Cyt-C与caspase在细胞凋亡中的作用及相互关系[J]. 中国老年学杂志,2011,31(15):2990-2992.
[24]刘晓婷,王延让,张明. 线粒体介导细胞凋亡的研究进展[J]. 环境与健康杂志,2013,28(2):182-185.
[25]Cande C, Cohen I, Daugas E, et al. Apoptosis-inducing factor (AIF): a novel caspase-independent death effector released from mitochondria. Biochimie. 2002;84(2-3): 215-222.
[26]Zou H, Li Y, Liu X, et al. An APAF-1.cytochrome c multimeric complex is a functional apoptosome that activates procaspase-9. J Biol Chem. 1999;274(17): 11549-11556.
[27]Hu Y, Benedict MA, Ding L, et al. Role of cytochrome c and dATP/ATP hydrolysis in Apaf-1-mediated caspase-9 activation and apoptosis. EMBO J. 1999;18(13):3586-3595.
[28]Saleh A, Srinivasula SM, Acharya S, et al. Cytochrome c and dATP-mediated oligomerization of Apaf-1 is a prerequisite for procaspase-9 activation. J Biol Chem. 1999;274(25):17941-17945.
[29]Brentnall M, Rodriguez-Menocal L, De Guevara RL, et al. Caspase-9, caspase-3 and caspase-7 have distinct roles during intrinsic apoptosis. BMC Cell Biol. 2013;14:32.
[30]Hirota M, Ito T, Okudela K, et al. Cell proliferation activity and the expression of cell cycle regulatory proteins in oral lichen planus. J Oral Pathol Med. 2002;31(4):204-212.
[31]Sutton VR, Davis JE, Cancilla M, et al. Initiation of apoptosis by granzyme B requires direct cleavage of bid, but not direct granzyme B-mediated caspase activation. J Exp Med. 2000; 192(10):1403-1414.
[32]Sitailo LA, Tibudan SS, Denning MF. Activation of caspase-9 is required for UV-induced apoptosis of human keratinocytes. J Biol Chem. 2002;277(22):19346-19352.
[33]Wurstle ML, Laussmann MA, Rehm M. The central role of initiator caspase-9 in apoptosis signal transduction and the regulation of its activation and activity on the apoptosome. Exp Cell Res. 2012;318(11):1213-1220.
[34]李志恒. 大鼠颅脑损伤后Caspase-9、MMP-3和NGB表达变化的研究[D]. 乌鲁木齐:新疆医科大学,2012.
[35]Guerrero AD, Schmitz I, Chen M, et al. Promotion of Caspase Activation by Caspase-9-mediated Feedback Amplification of Mitochondrial Damage. J Clin Cell Immunol. 2012;3(3). pii: 1000126.
[36]Chavez-Galan L, Sada-Ovalle I, Baez-Saldana R, et al. Monocytes from tuberculosis patients that exhibit cleaved caspase 9 and denaturalized cytochrome c are more susceptible to death mediated by Toll-like receptor 2. Immunology. 2012;135(4):299-311.
[37]Wang YJ, Niu XP, Yang L, et al. Effects of celecoxib on cycle kinetics of gastric cancer cells and protein expression of cytochrome C and caspase-9. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2013; 14(4):2343-2347.
[38]Fang F, Gong PS, Zhao HG, et al. Mitochondrial Modulation of Apoptosis Induced by Low-dose Radiation in Mouse Testicular Cells. Biomed Environ Sci. 2013;26(10):820-830.
[39]刘江涛,郭雄,吴翠艳,等. 线粒体细胞色素c介导的caspase-9激活通路参与大骨节病关节软骨细胞凋亡的发生机制[J]. 西安交通大学学报:医学版,2011,32(5):580-584.
[40]曹军军,杨茂伟,郭宝磊,等. 高糖通过线粒体途径诱导成骨细胞凋亡[J]. 中国生物化学与分子生物学报,2012,28(12): 1109-1114. |
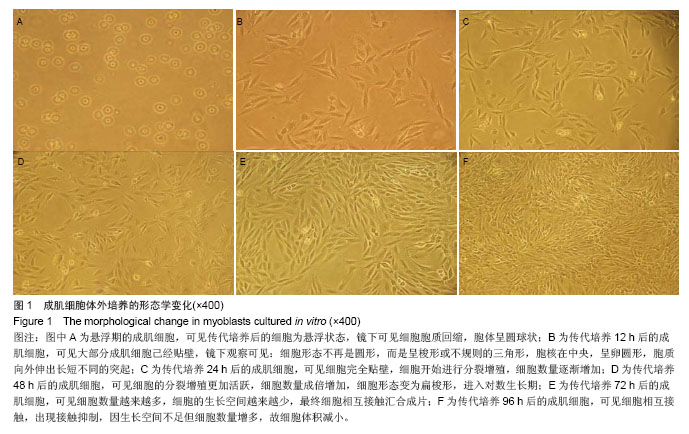
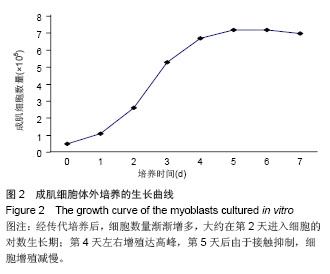
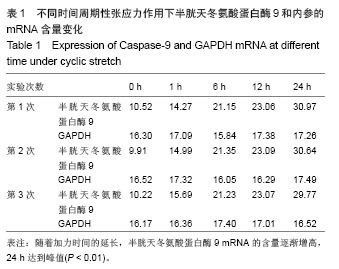
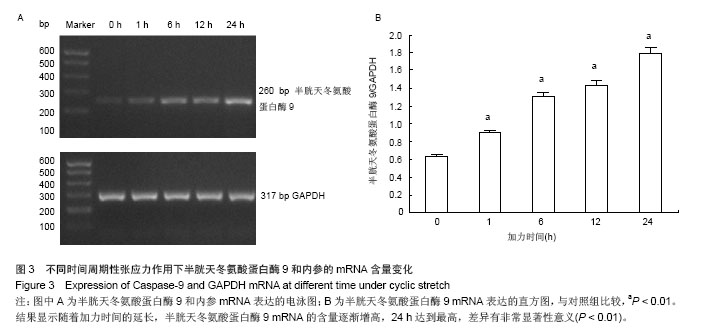
.jpg)
.jpg)